I haven’t been writing much in the blog these past few years as communication seems to come mostly through instagram. I miss the longer form of writing and putting an entry together. This was a past piece that I often return to. To see how I am doing perhaps. To make sure I don’t stray too far? Sketches from this post keep appearing in publications including the “Pretty Good House” book.
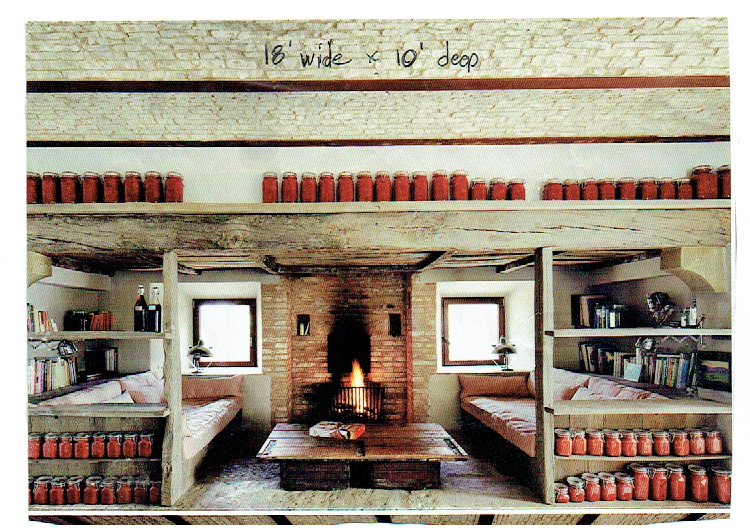
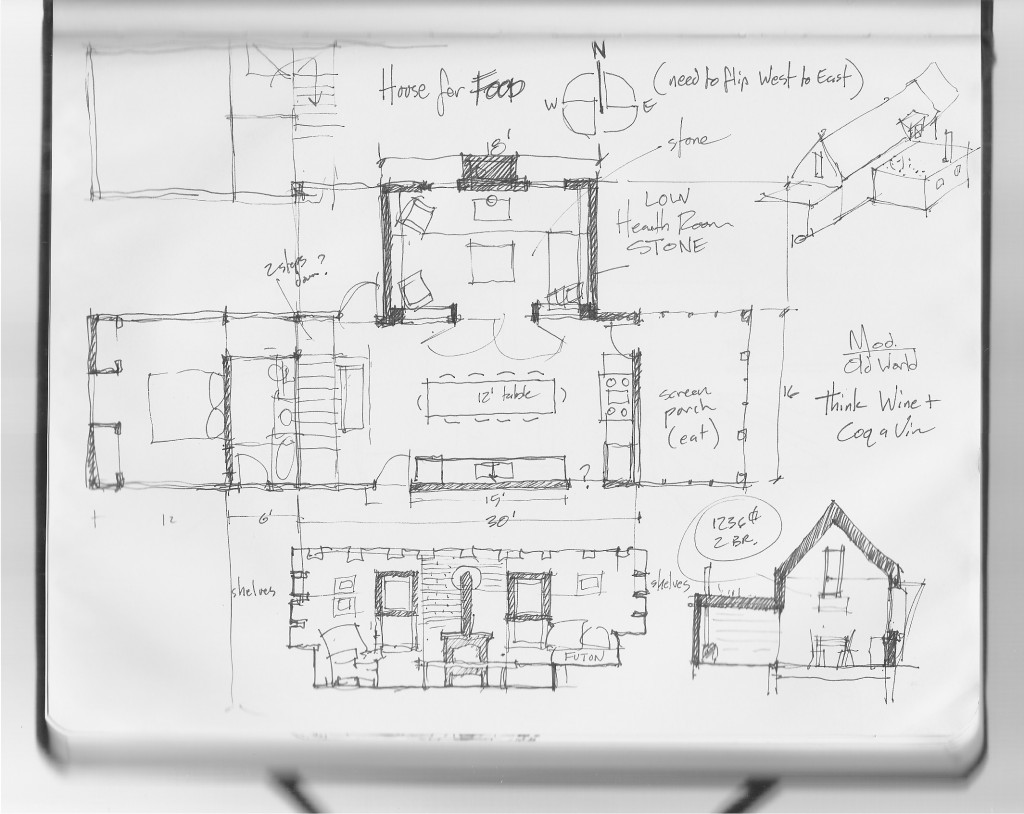
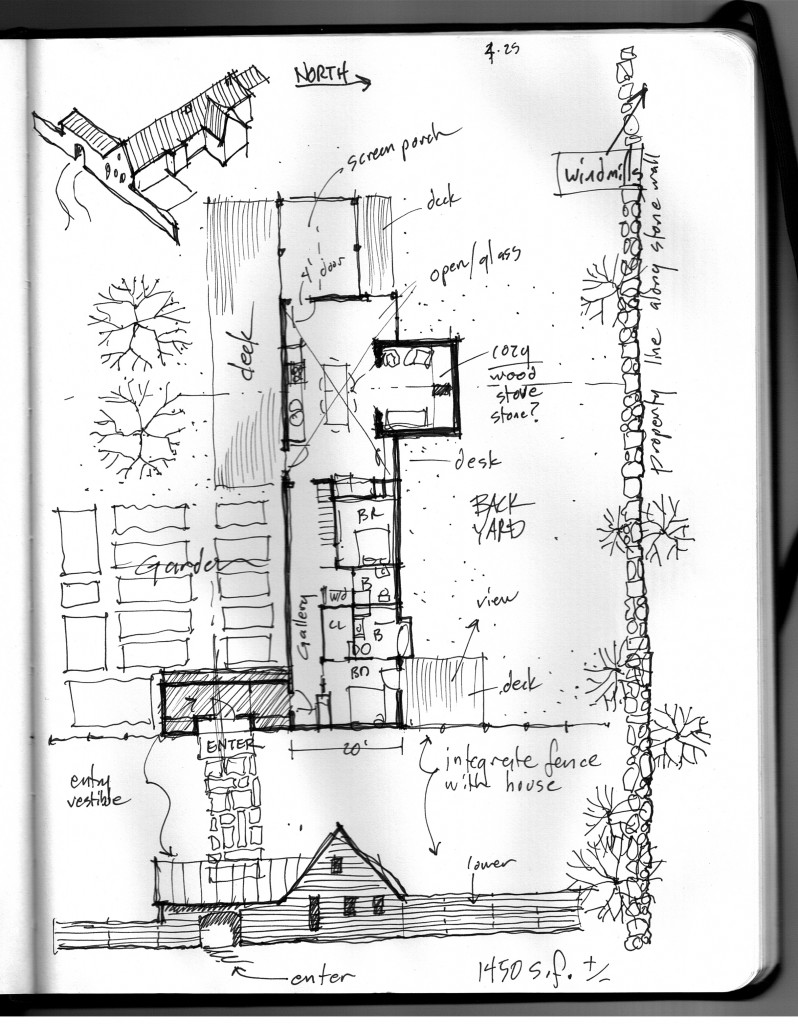
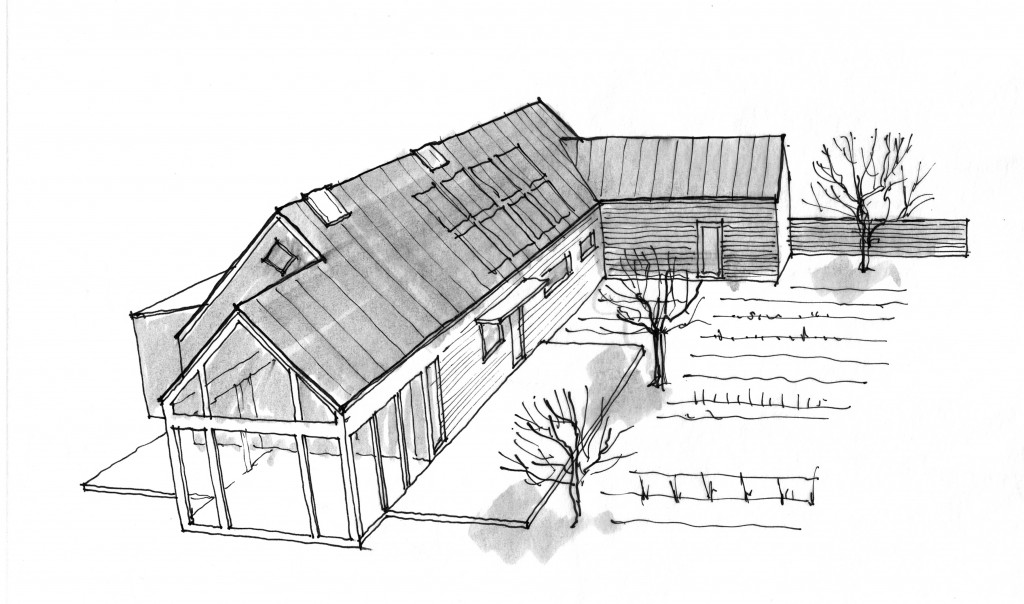
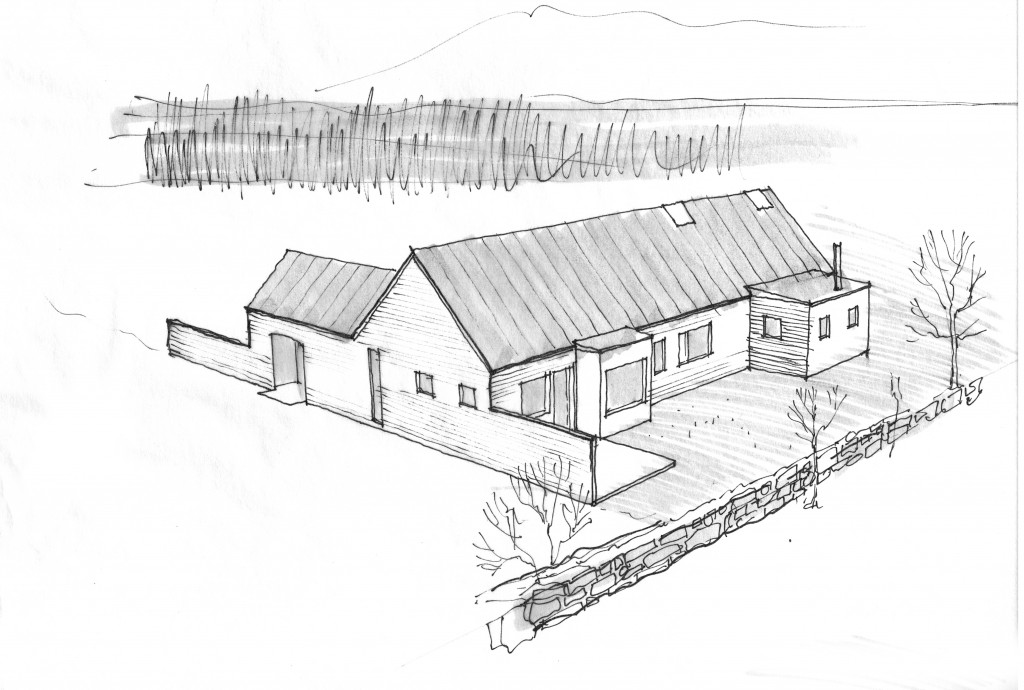
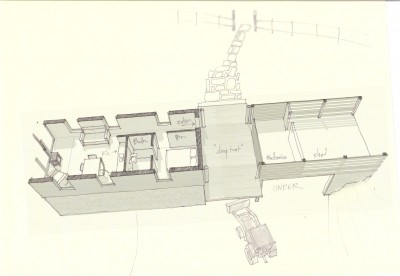
A House for Slow LivingThe original concept came to me in a dream (yes – I dream architecturally) I think the dream may have been generated by this image which has been on my bulletin board fora few years: The original sketch was called “a house for food”
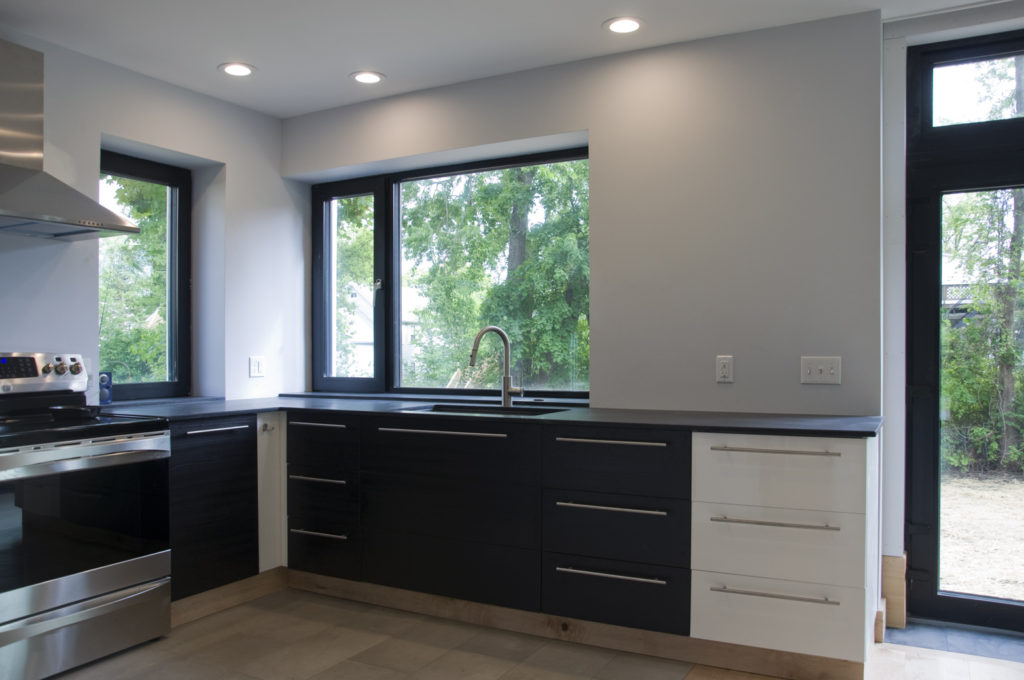
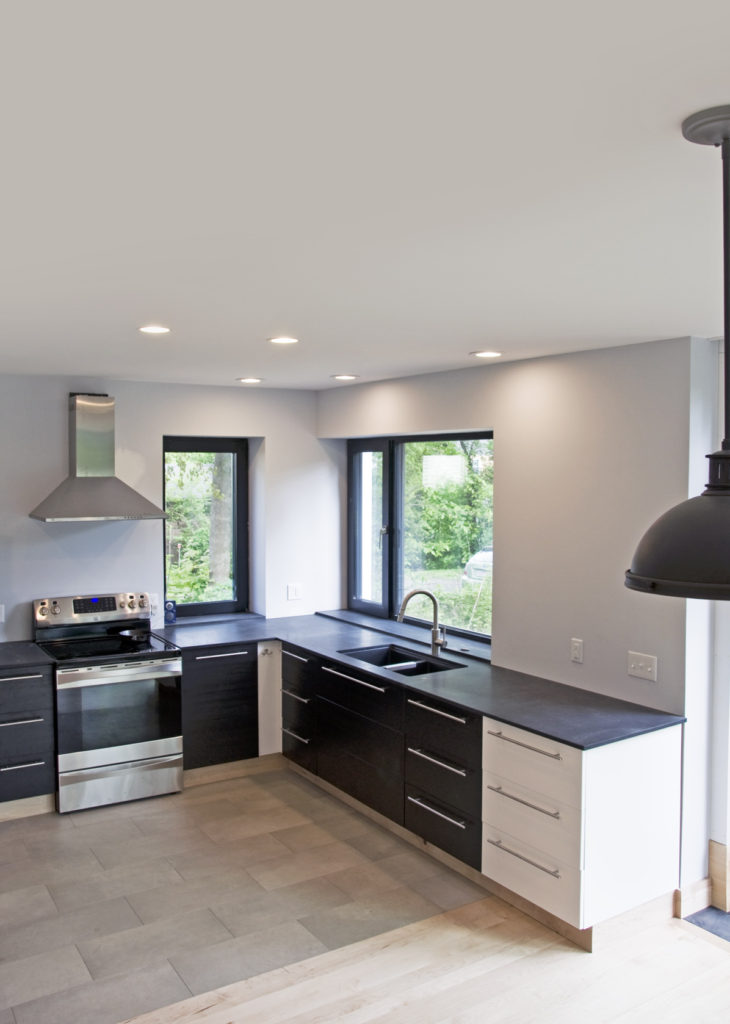
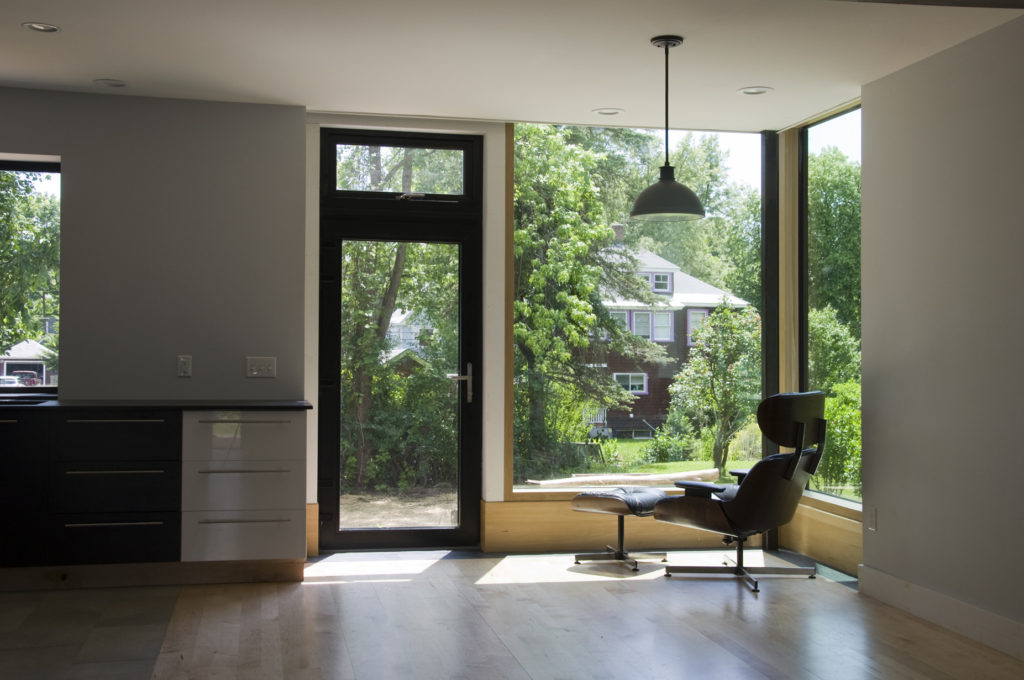
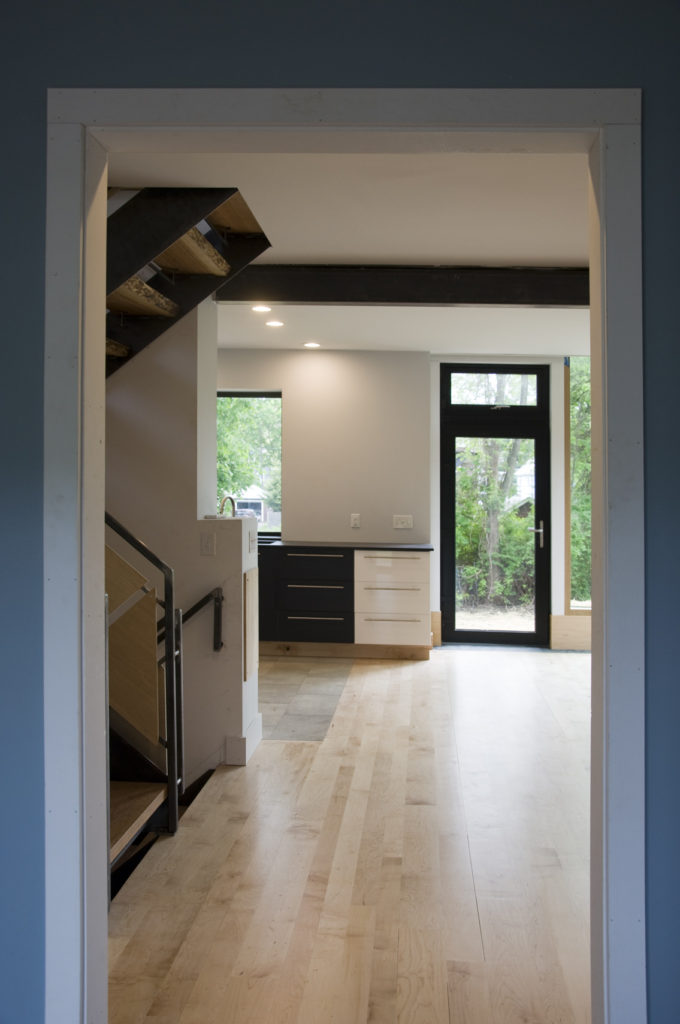
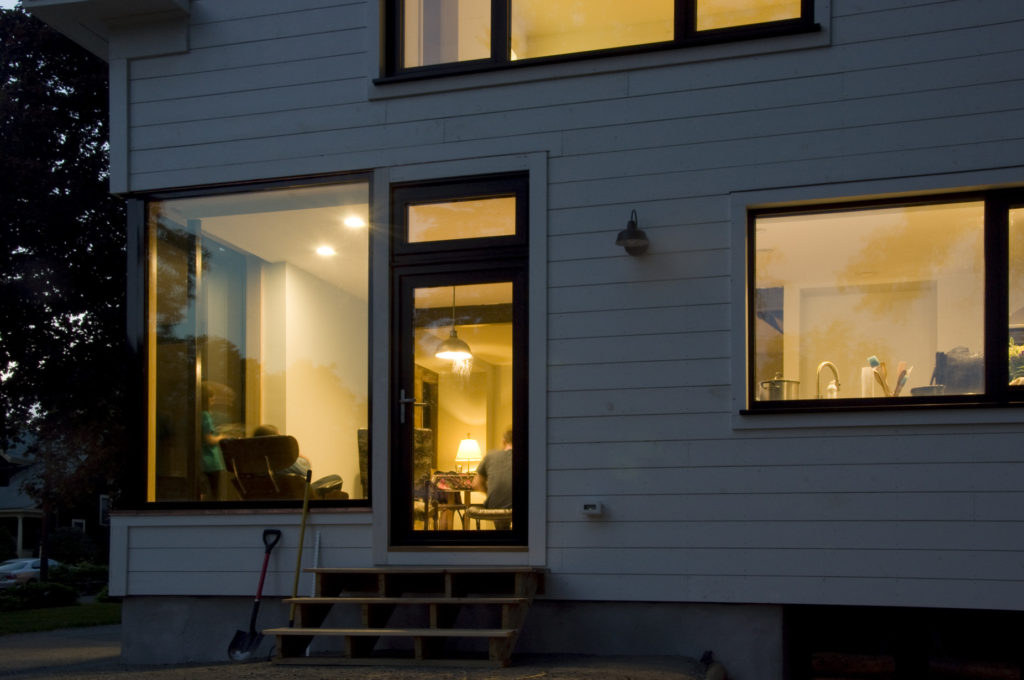
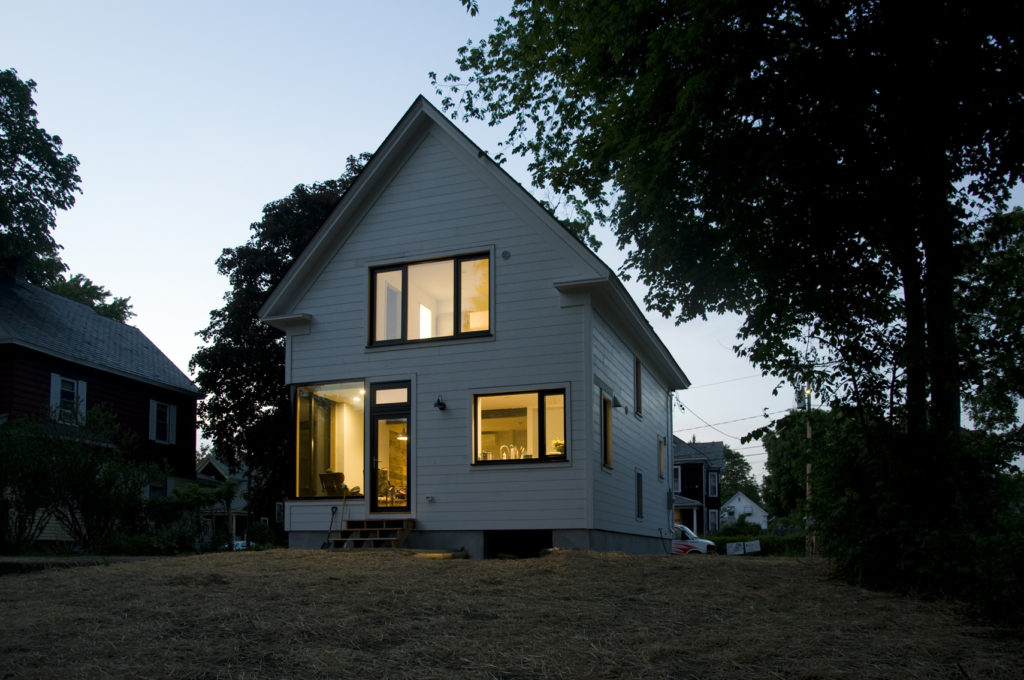
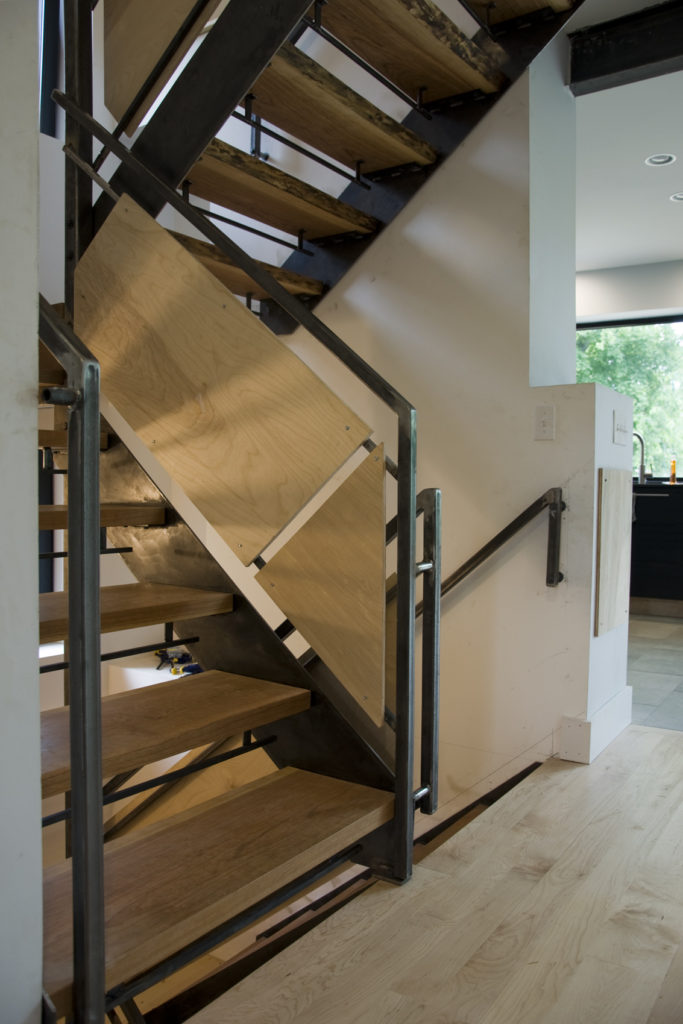
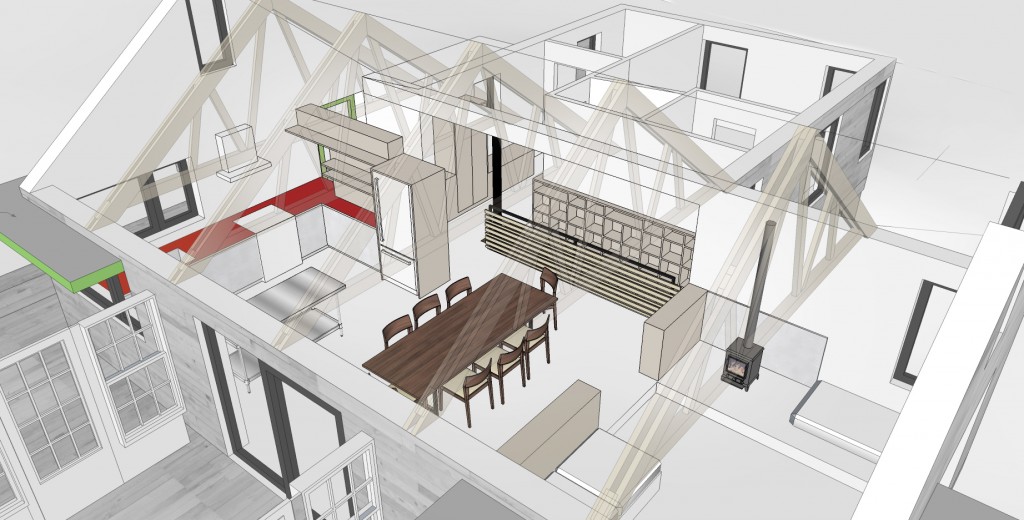
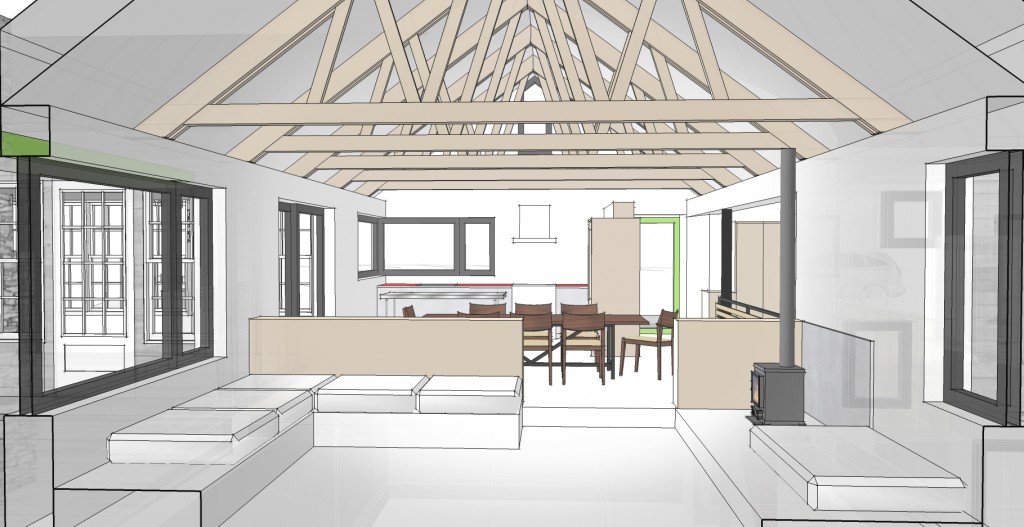
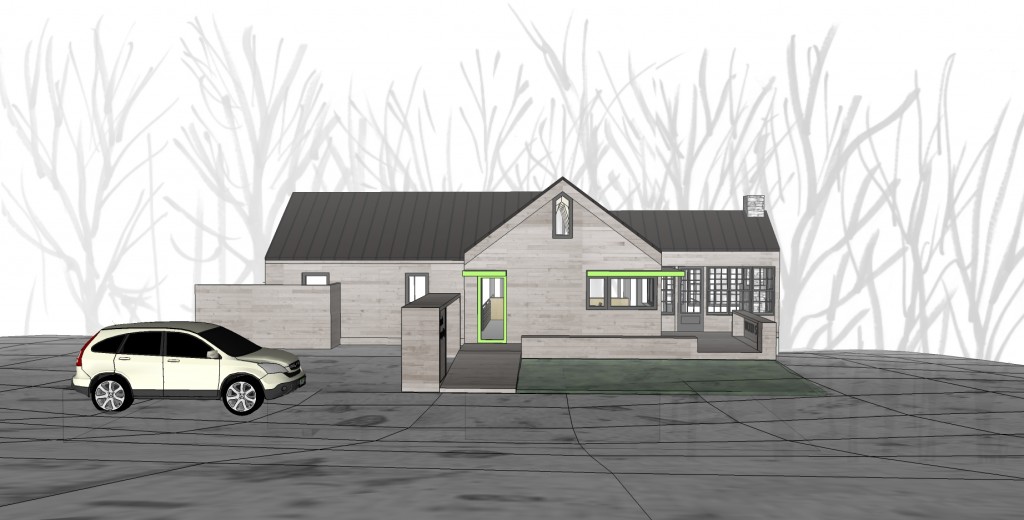
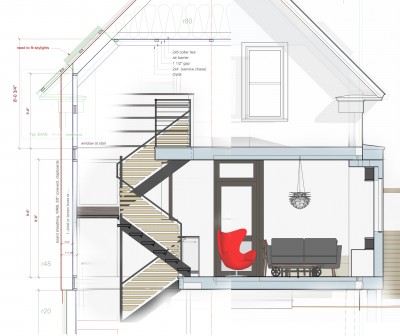
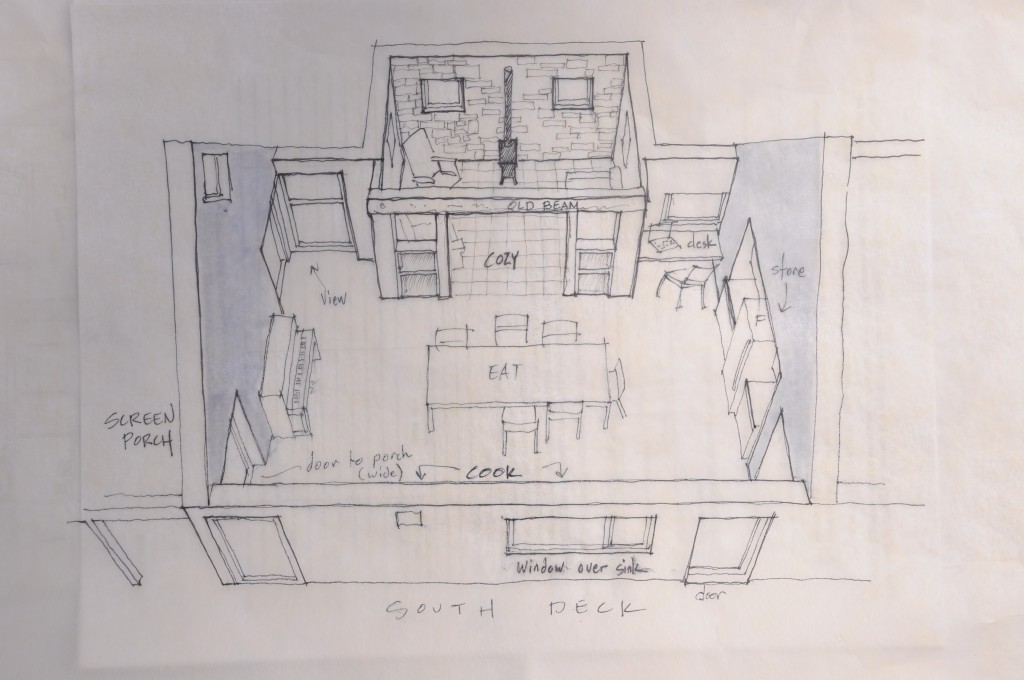
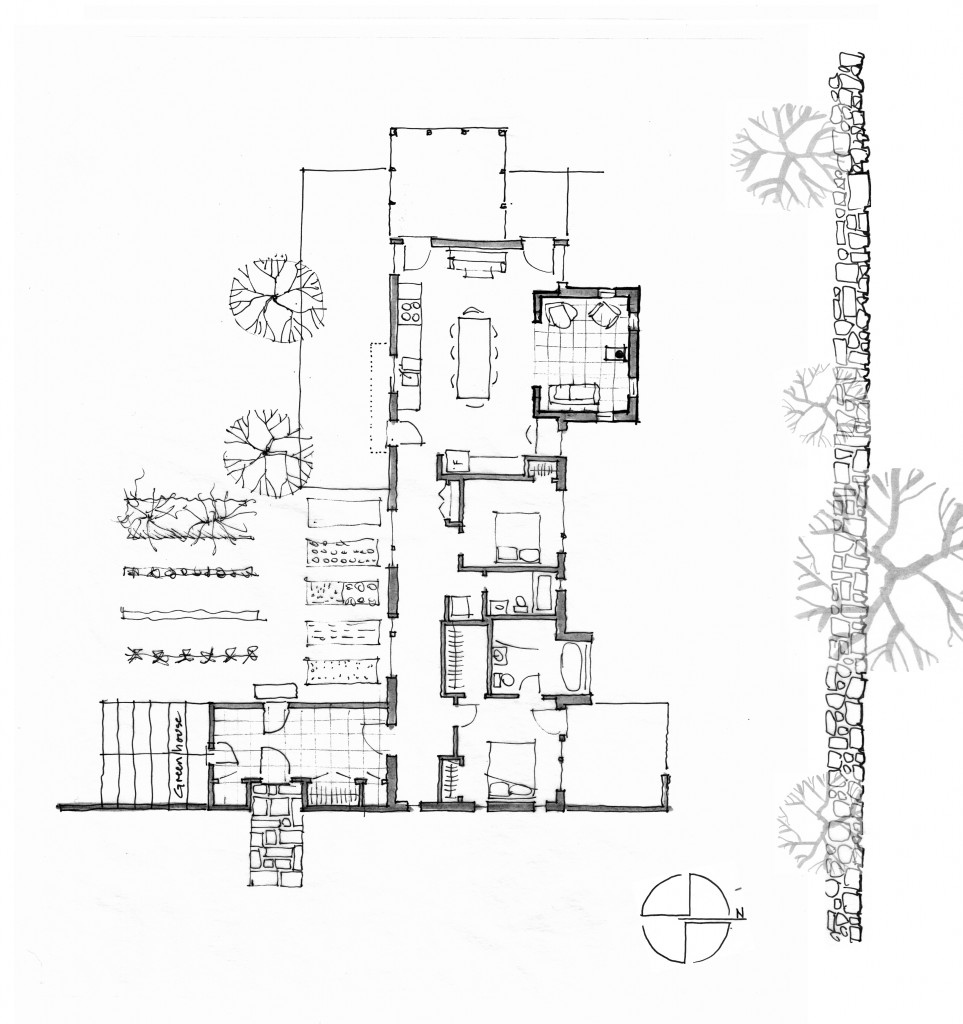
The core concept was centered around the growing, preparation and consumption of food which lends itself to the idea of gatherings of family and friends and leads to the notion of how to live in a close relationship to the local environment. From my own experience I drew upon the old fashioned ideas of hunkering down by the fire on a cold winter evening, opening the house up to the sounds, smells and breezes of a summer day, “putting food by” and making routine preparations for winter in the Autumn, starting seedlings on a windowsill in the spring, caring for children or elders. Also, how can we appreciate the beauty of the winter landscape and light without feeling overcome by it. This is a common issue in the Northeast. Where do you sit to watch a thunderstorm rolling in or to watch the snow fall? Music! – not just acoustics but around here, everybody is also a musician. How does that fit into our daily lives? Much inspiration is to be found in images and stories depicting rural life from previous times in Europe and America. I am drawn to the imagery of hard working English country houses where the real life of the house centers between the kitchen and the door stoop leading directly to the working yard and gardens. Think: Peter Rabbit in Mr. McGregor’s Garden by Beatrix Potter with a potting shed, cold frames and lots of cabbages. I am fascinated by early New England farms and town dwellings and how lives were played out in them. Not the big events but the little, day to day, season to season routines. Light and fresh air are celebrated and sought after and even, perhaps, taken for granted in an age before television and telephones. Materials are worn but durable, practical and show their age and history and that is where their beauty lies.
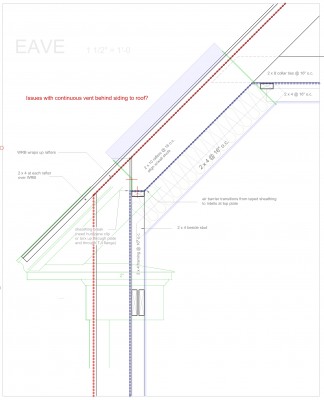
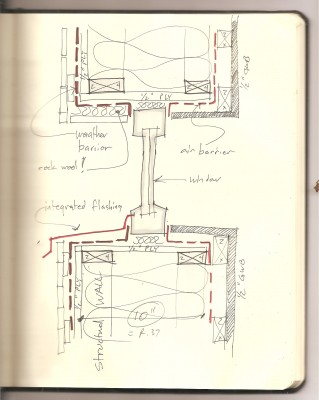
The Building Science aspect of design and detailing that we are all so immersed in lately addresses the idea of being able to lock the door and walk away for a month in the winter and not worry about much of anything. The neighbor has the key and will water the plants. Building Science addresses being what we are calling “net zero” so you are not storing and burning fossil fuel on site and paying for it as well. Building Science addresses the notion of simplicity – who needs a heating system that could go on the fritz and bust your pipes and freeze all your house plants so when your neighbor comes over to water the house plants, he finds an awful mess and has to call you in some recently devastated country where you are doing relief work. Building Science allows you to return in March to a house filled with fresh air and no mildew. (building science can’t help with what you left in the fridge) Building Science can free you from many previously taken for granted maintenance issues and expenses such as painting and periodic repair, maintenance and replacement of the mechanical parts of the house because now you have fewer and simpler systems.
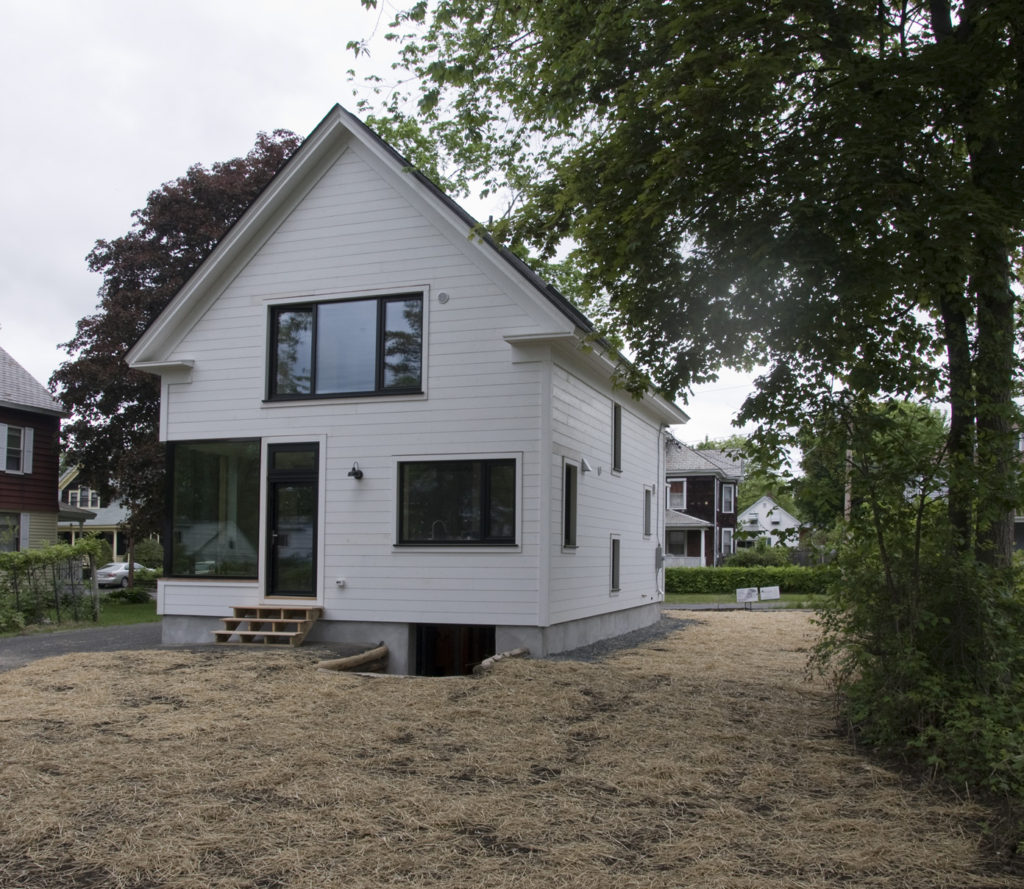
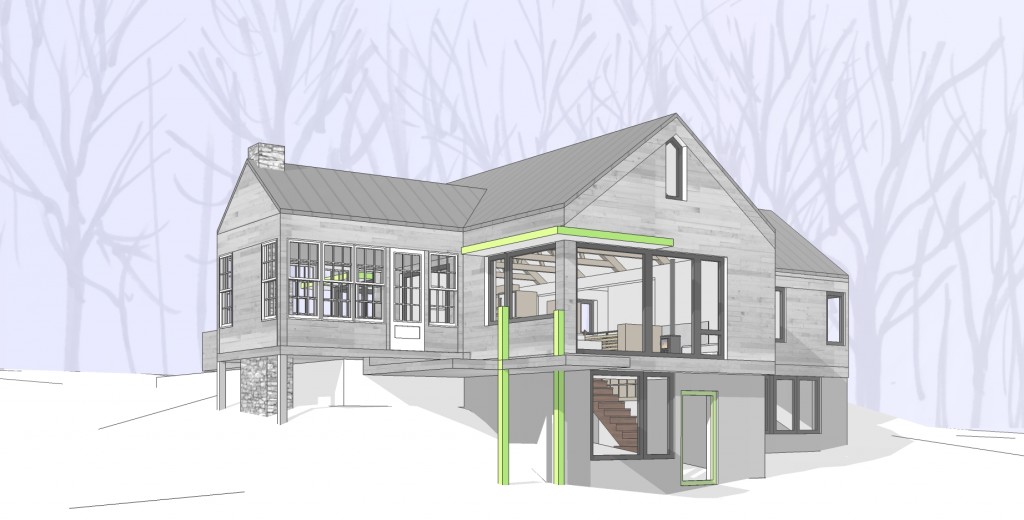
How then, to marry my heady and romantic thoughts with the physics of modern building science? How do I pack all of this sensuality and feeling into a house that celebrates the process of living this chosen life rather than reminding one of the potentially inherent drudgery? Since these ideas are very personal to me, it isn’t very difficult to make a series of design moves and decisions that bring me pretty close. I have been moving in this direction for much of my life. I am often “pretty close” but getting to that higher level is tricky and elusive. I’m not there yet with this design but it’s still early….
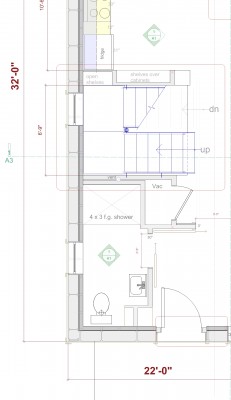
In this design, I'm trying to balance small and simple with a richness of space that goes far beyond light and shadow, a good floor plan and simplicity of form and add my own interpretation of what it can mean to live in Vermont and lead a life integrated with the climate and culture of the place. I'm drawing heavily on history and my own sense of aesthetics as well as all my cumulative observations and experience.
Dang! Maybe I should tear down my own house and build something like this!
For those interested in the Slow Living Movement, Brattleboro has a Slow Living Summit coming up in June associated with the Strolling of the Heiffers parade and festival.